Test Progress

All answers to be rounded off to 2 decimals.
An option can be use more than once.

An option can be use more than once.

Type in the correct letter from the options above:

All answers to be rounded off to 2 decimals.
An option can be use more than once.

An option can be use more than once.

Type in the correct letter from the options above:

All answers to be rounded off to 2 decimals.
An option can be use more than once.

An option can be use more than once.

Type in the correct letter from the options above:
You need to make at least one attempt at answering all the questions in the test before you can look at the answers.
Loading progress report...
Absolute Zero
The lowest possible temperature that can be achieved.
Absorption spectrum
A spectrum that forms when a cool gas selectively absorbs certain wavelengths from the white light spectrum.

Accelerated motion
Motion where the speed of the object changes. If it goes faster the acceleration is positive. If it goes slower (decelerate) the acceleration is negative.
Acceleration
The rate of change of velocity.

Acid
An acid is a proton donor. It also is a substance that can neutralise a base.
Acid-base reaction
A reaction where a transfer of proton(s) from the acid to the base takes place.

Activated complex
A temporary transition state between the reagents and the products.
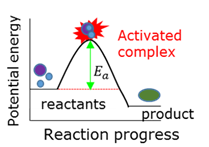
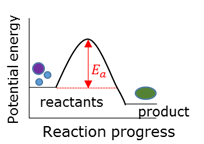
Activation energy
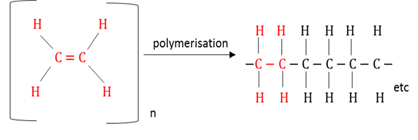
Addition polymer
A polymer that forms when monomers (that usually contain double bonds) combine through addition reactions.
Addition polymerisation
A chemical reaction during which unsaturated monomers (carbohydrates containing double or triple bonds) join to each other to form long chain structures (polymers).
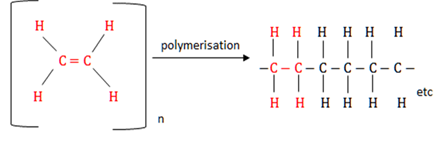
Addition reaction
The double or triple bonds in unsaturated hydrocarbons are broken when other atoms are added to the carbon atoms between which the bonds existed and no other by-products are formed.

Adsorbsion
The phenomenon that molecules tend to stick to the surface of a substance.
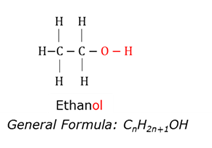
Alcohol
Organic compound with a hydroxile (OH-) functional group bonded to a carbon atom.
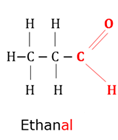
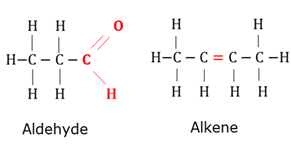
Aldehyde
Organic compound with (-CH=O) as functional group bonded to the carbon chain.
Aliphatic hydrocarbons
In organic chemistry hydrocarbons are divided into two classes - aliphatic and aromatic. Aliphatic hydrocarbons include straight, branched and cyclic chains, but cyclic aliphatic compounds exclude benzene structures.
Alkali
An alkali is a base that is soluble in water.
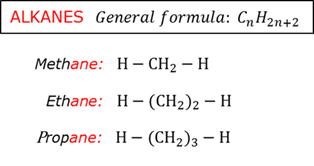
Alkane
Organic compounds with only single bonds between the carbon atoms.
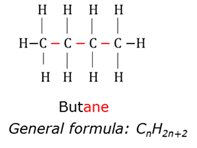
Alkene
Organic compounds that has at least one double bond between two carbon atoms.
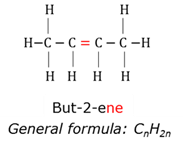
Alkyne
Organic compounds that has at least one triple bond between two carbon atoms
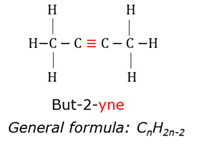
Alloy
Homogeneous solid mixture of two or more metals where the atoms of one metal fill the open spaces in between the atoms of the base metal.
Alpha particle
A radio active particle made up of two protons and two neutrons - a helium nucleus.
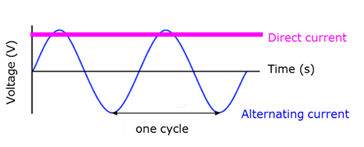
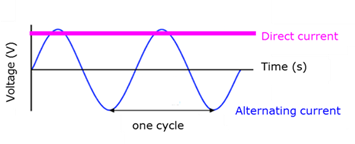
Alternating current
(AC) - Electric current where the flow direction of the charge changes with a fixed frequency.
Ammeter
An instrument to measure the current (I) through a given circuit element.

Ampere (A)
The unit for current strength (I = Q/t).
Ampholyte
A chemical substance that can react as either an acid or a base. It can therefore donate or accept protons.
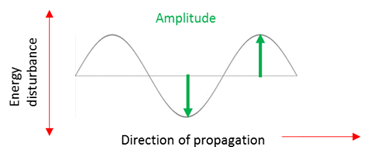
Amplitude
The disturbance of a particle from the rest/equilibrium position.
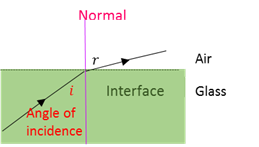
Angle of incidence
The angle (i) between the incident beam and the normal.
Angle of reflection
The angle (r) between the reflected beam and the normal.

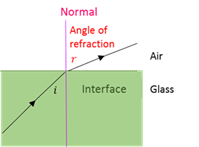
Angle of refraction
The angle (r) between the refracted beam and the normal.
Anhydrous
Without water.
Anion
An atom that has gained one or more electrons to form a negative ion.

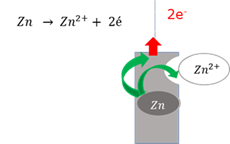
Anode
The electrode where oxidation takes place - electrons leave the electrode.
Aqueous solution
A weak solution with water as solvent.
Aromatic hydrocarbons
In organic chemistry hydrocarbons are divided into two classes - aliphatic and aromatic. Aromatic hydrocarbons have a ring structure like benzene.

Arrhenius theory
An acid is a substance that produces hydrogen ions / hydronium ions when dissolved in water. A base is a substance that produces hydroxide ions when dissolved in water.

Atmosphere
The gaseous layer that encompasses the lithosphere.
Atmospheric pressure
The pressure exerted by the gas molecules that make up the atmosphere at a given place.
Atom
The smallest part of an element that has all the chemical characteristics of that element.
Atomic number
Atomic number (Z) represents the number of protons in the nucleus of an atom.
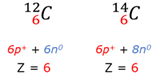
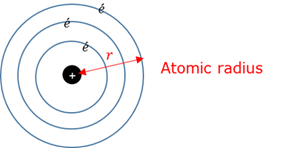
Atomic radius
A measurement of the size of an atom, taken from the nucleus to the outermost electron orbital.
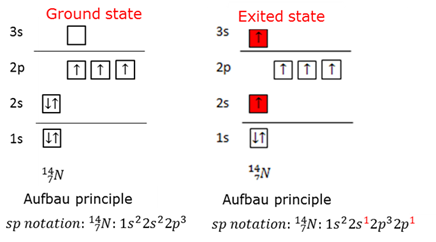
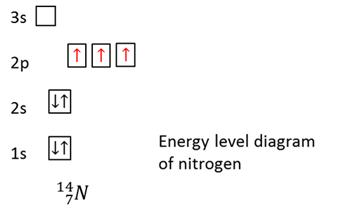
Aufbau principle
The order in which electrons fill the orbitals. Start with lowest energy level. First unpared before paring takes place.
Auto-ionisation of water
When a water molecule spontaneously reacts with another water molecule.

Average speed
A scalar quantity of distance travelled divided by the time.
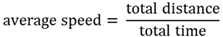
Average velocity
A vector quantity of displacement divided by the time taken for the change.

Avogadro's gas law
The volume (V) of a gas is directly proportional to the number of moles (n) of the gas at contant temperature and pressure.
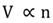
Barometer
An instrument that measures atmospheric pressure.
Base
A base is a proton acceptor. It is also a substance that can neutralise an acid.
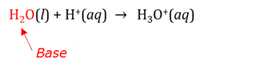
Biosphere
The biosphere is the lithosphere, hydrosphere and atmosphere, including all the living organisms on earth.
Bohr model
Bohr proposed a model of the atom consisting of a small positively charged nucleus in the middle, which is surrounded by negatively charged particles (electrons) moving in specific circular orbits around the nucleus.
Boiling point
The temperature at which a substance changes phases from liquid to gas at standard atmospheric pressure. The physical point of boiling of a liquid is when the vapour pressure = the atmospheric pressure and will be different at different atmospheric pressures.

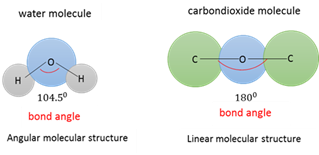
Bond angle
The angle between two atoms that are bonded to a central atom.
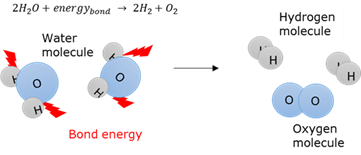
Bond energy
The amount of energy needed to break a bond between two atoms in a molecule.
Bond forces
The different intramolecular forces that keep atoms together in a molecule
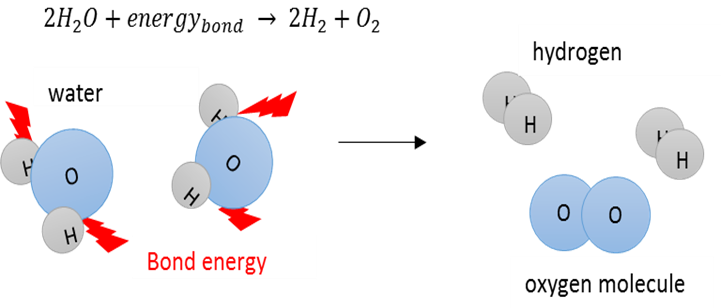
Bond length
The distance between the nuclei of two bound atoms.
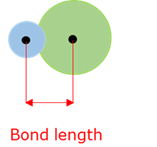
Boyle's law
The volume (V) of an enclosed mass of gas is inversely proportional to the presssure (p) thereof, at a constant temperature.
Brittle
A property of certain materials that they are hard, but break easily.
Brownian motion
The spontaneous and random movement of microscopic particles in liquids and gases due the their collisions against each other in the medium.

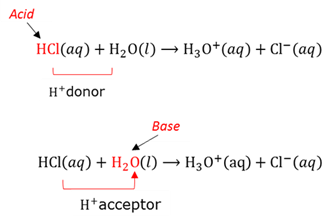
Brønsted-Lowry theory
An acid is a proton donor - It will release protons in the presence of a base. A base is a proton acceptor - It will accept protons in the presence of an acid.
Carbohydrate
Compounds consisting of only carbon and hydrogen.
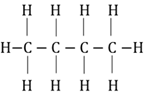
Carbonyl group
A functional group in organic chemistry composed of a carbon atom double-bonded to an oxygen atom.
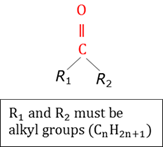
Carboxyl group
A functional group in organic chemistry consisting of both a carbonyl and a hydroxyl group (-COOH) attached to the same carbon atom.
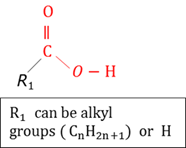
Carboxylic acid
An organic compound that contains a carboxylgroup (-COOH).
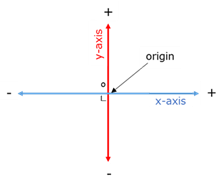
Cartecian plane
Flat surface with an x-axis and a y-axis as perpendicular reference lines.
Catalyst
A catalyst changes the rate of a reaction without becoming part of the reaction.
Cathode
The electrode where reduction takes place - electrons enter the electrode.

Cation
An atom that has lost one or more electrons to form a positive ion.
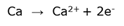
Cell notation
A concise way to represent the reactions in an elektrochemical cell. The anode and cathode are separated by two vertical lines which represents the salt bridge. The oxidation reaction (at the anode) is written left of the lines and the reduction reaction (at the cathode) is written right of the lines.

Cell potential (emf)
The cell potential (emf) is a measurement of the ability of a cell to provide energy. The emf of a battery is the total energy per coulomb that is transferred to the charges in the external circuit PLUS the energy per coloumb transferred to the charges while they are moving through the battery. (Emf = voltages across the external circuit plus the voltage across the internal resistance of the cell)
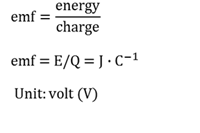
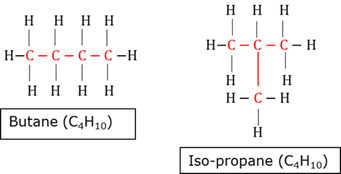
Chain isomers
Molecules that have the same molecular formulae, but different chain structures.
Charles law
The volume (V) of a given mass of gas is directly proportional to the absolute temperature (T) of the gas at constant pressure.
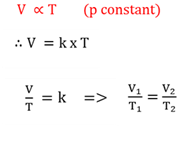
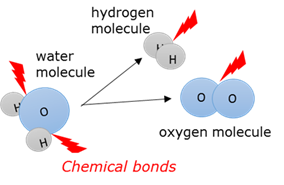
Chemical bond
The force that keep the atoms together in a molecule.
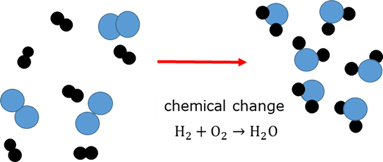
Chemical change
A permanent change in the chemical nature and composition of a substance to form a new substance.
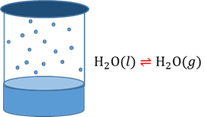
Chemical equilibrium
The point in a chemical reaction where the forward reaction takes place at the same rate as the reverse reaction. Although the raction is still continuing the concentrations of the reagents and products do not change any more.
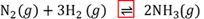
Chemical properties
The properties of a substance that makes it unique and which can only change if the substance undergoes a chemical change.
Chemical reaction
In chemical reactions substances react with each other to form new substances. The chemical composition and properties of the new products are different to that of the reagents.
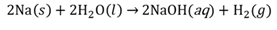
Closed chemical system
A system where the total mass of the system remains constant during a chemical reaction, but energy transfer between the system and the surroundings can still take place.
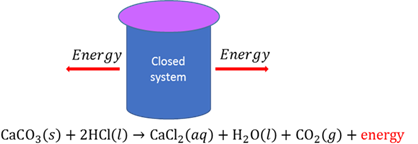
Closed circuit
A circuit is closed when an electric current can flow uninterrupted through the circuit.

Coherent sources
Sources of light which emit continous light waves of the same wavelength and frequency and where the light waves are in phase (laser).
Collision theory
A model that explains rate of reaction as the result of particles that collide with a certain minimum energy.
Combustion
An exothermic reaction between a substance and oxygen.
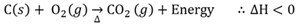
Combustion of alkanes
An exothermic reaction between an alkane and oxygen. Normally this is a non-spontaneous reaction that requires activation energy to start the reaction.
Compass
A compass indicates the direction of a magnetic field because the compass needle always points North.

Compound
A pure substance that constist of 2 or more different atoms.
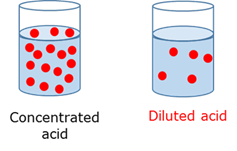
Concentrated acid
Contains a large amount of acid substance per unit volume of the solution.
Concentrated Base
Contains a large amount of base substance per unit volume of the solution.
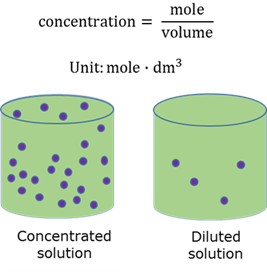
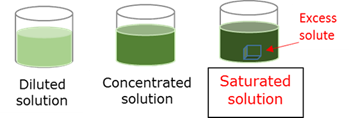
Concentrated solution
A solution containing a relative large amount of solute per unit volume of solvent.

Concentration of a solution
The number of moles of solute per unit volume of the solution.
Condensation
A physical reaction when a substance changes from gas phase to liquid phase.
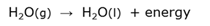
Condensation polymerisation
A chemical reaction where monomers with different functional groups react with each other to form a long chain with the emission of smaller molecules, usually water.

Condensed structural formula
Shows the most important/functional groups in an organic molecule in detail and the rest in condensed form.

Conductivity
The degree to which a specific material conducts electricity or heat.
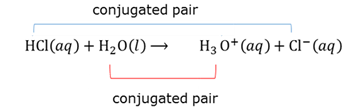
Conjugated acid-base pairs
A conjugated acid-base pair is where a reagent and a product only differs in the number of H+ they have.
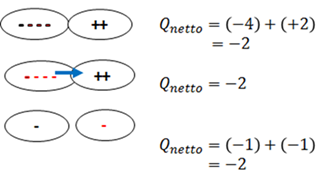
Conservation of charge
The net charge (Qnet) of an isolated system remains constant during any physical process. In the example - two charges make contact and then separate.
Conservation of energy
The total energy in a system cannot be created or destroyed, only be transformed from one form into another form.
Conservation of mass
The total mass of the reagents and the products in a closed system will remain the same, irrespective of the reactions that take place in the system.
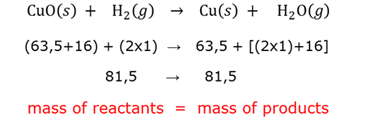
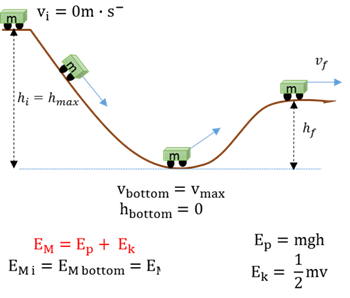
Conservation of mechanical energy
The total mechanical energy (EM = sum of gravitational potential energy and kinetic energy) in an isolated system remains constant.
Conservation of momentum
The total linear momentum of an isolated system remains constant (is conserved).
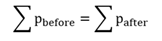
Conservative forces
A conservative force is one where the work done to move an object from one point to another point is independent of the route taken. Thus the net work done by a conservative force to move an object around a closed path (starting and ending at the same point) is zero.
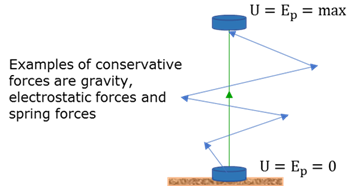
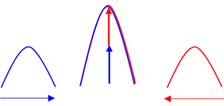
Constructive interference
When two waves cross each other in such a way that the crest of the one wave meets the crest of the other wave, the result is an increase in the amplitude (superposition).
Contact force
The force that an object exerts on another object when they are in contact with each other.
Contact process
The industrial process for producing sulfuric acid.
Continuous spectrum
The complete electromagnetic spectrum that contains all the wavelengths (white light).

Conventional current
Opposite to electron current. The direction that positive charges will flow in a conductor.
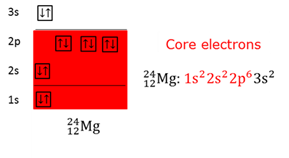
Core electrons
The electrons that are found in the inner completely filled energy levels.
Coulomb
The unit of electric charge. 1 Coulomb is the charge that moves through a conductor if a current of 1 ampere flows for 1 second.
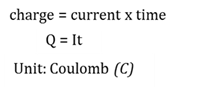
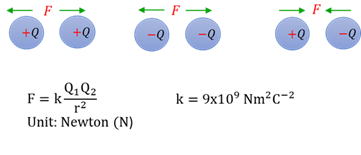
Coulomb’s law
The force between two charges is directly proportional to the product of the charges and inversely proportional to the distance between them squared.
Couper structure
Atomic structure that only shows the covalent bonds between atoms, with the bonding electrons depicted as lines.
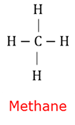
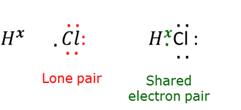
Covalent bond
A bond where at least one pair of electrons are shared between two atoms.

Covalent bond - non polar
Bond where the bonding electrons are shared equally between the atoms.
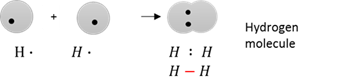
Covalent bond - polar
Bond where the bonding electrons are not equally shared between the atoms and leads to the forming of a dipole.
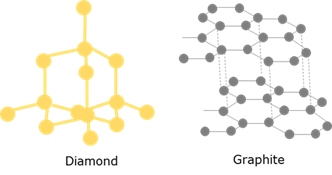
Covalent network structures
Covalent network structures consist of giant repeating lattices of covalently bonded atoms. Found in diamond, graphite, SiO₂ and some boron compounds.
Cracking
A chemical process where long carbon chains are broken down into smaller molecules.

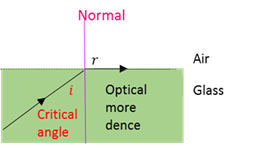
Critical angle
That angle of incidence that produces an angle of refraction of 90° when light passes from an optical more dense medium to an optically less dense medium.
Crystal lattice
Three dimensional regular repeating pattern of atoms, molecules or ions in a crystaline substance.
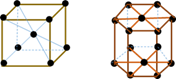
Crystal water
Water that forms part of the crystal structure of certain salts.
Current strength
The rate at which charge flows.
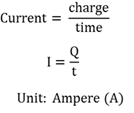
Cut-off potential
The minimum reverse potential that has to be applied across a photo-cell to just stop the flow of the current.
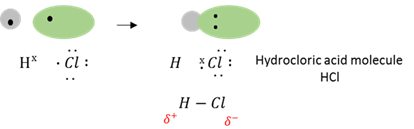
Dative covalent bond
A bond that forms when an atom with an incomplete complement of electrons in its valence shell can share a lone pair of electrons donated by another atom to form a molecule .
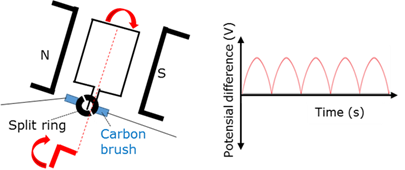
DC Generator
Generator that produces a direct current (DC) because it has only one split ring.
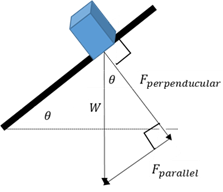
Decomposing a vector
Breaking a vector down into two perpendicular components.
Decomposition
A reaction in which a complex compound is broken down into simpler substances. One method is through electrolysis.
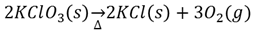
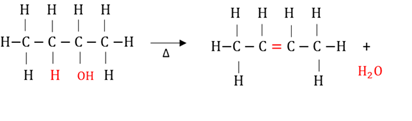
Dehydration of alcohols
The elimination of a hydroxyl (OH) group and a hydrogen atom (H) from adjacent carbon atoms to form an alkene and water. Heat is needed for the reaction to take place.
Dehydro-halogenation
The elimination of hydrogen and a halogen from a haloalkane to form an alkene and a hydrogenhalide.
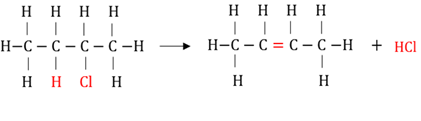
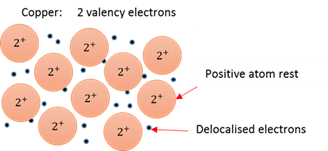
Delocalised electrons
Valence electrons that are not bound to a specific atom, but are shared between the atoms (metalic bonds).
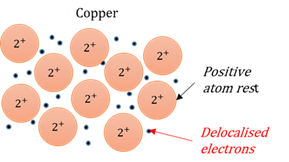
Density
The ratio of the mass of a substance to its voume. Also the number of atoms/molecules per unit volume
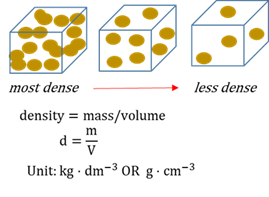
Dependent variable
The variable that changes as the independent variable changes. On a graph it always comes on the y-axis
Destructive interference
When two waves cross each other in such a way that the crest of the one wave meets the trough of the other wave, the result is a decrease in the amplitude.
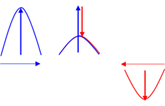
Diffraction
The ability of a wave to spread out in wave fronts as it passes through a small opening or around a sharp edge.
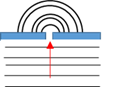
Diffusion
A physical reaction where a substance spontaneously moves from an area of higher concentration to an area where the substance is in lower concentration.
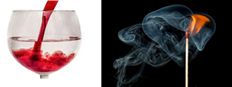
Diluted acid
Contains a small amount of acid substance per unit volume of the solution.
Diluted base
Contains a small amount of base substance per unit volume of the solution.
Diluted solution
A solution that contains a relative small amount of solute per unit volume of solvent.

Diode
An electronic component with the property that an electric current can only flow in one direction through it.
Diprotic acid
An acid that can donate two protons per acid molecule.

Direct current
(DC) - Electric current where the flow of charge is in one direction only.
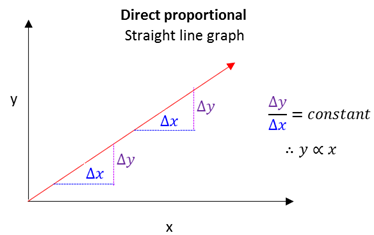
Directly proportional
When a change in one variable leads to an equal change in the other variable.
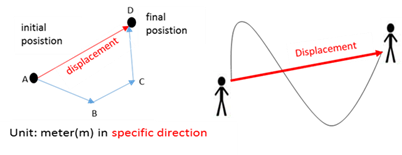
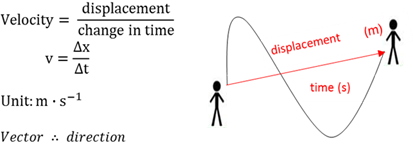
Displacement
A vector quantity depicting the net change in position from the initial to the final position.
Displacement reaction
A chemical reaction where an ion of a more reactive element replaces the ion of a less reactive element to form a new substance.
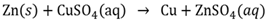
Dissociation
A reaction between a substance and water where bonds are broken to form hydrated ions.
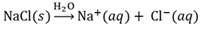
Dissolve
The process in which solid ionic crystals break up into ions in water.
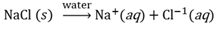
Distance
The actual path that an object follows to move from one point to another, taken along the route of movement.
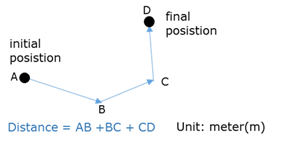
Doppler Effect
The phenomonen that the pitch or frequency of sound waves (or light waves ) as detected by a listerner, changes if the source of the waves and the observer move relative to one another. The source and the listener will then have different velocities relative to the medium of sound propagation.
Double bond
Covalent bond where two atoms share 4 electrons (two electron pairs).
Ductile
The property of metals that can be bent or pulled into different shapes.

Echos of sound waves
The reflection of sound waves from a surface. The time lapse between the sound and the echo is determined by the distance the sound wave has to travel forward and backward.
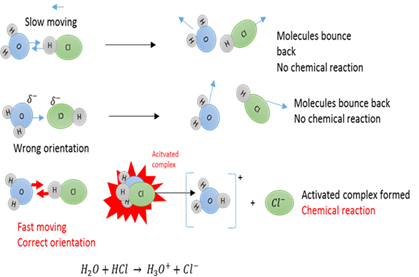
Effective collision
Effective collision between molecules will lead to an activated complex forming.
Elastic collision
A collision in which both momentum and kinetic energy are conserved.

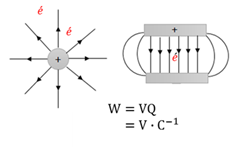
Electric field
The electrical field at a point is the electrostatic force experienced per unit positive charge placed at this point.

Electric field lines
Imaginary lines that indicate the direction in which a positive test charge will move if it is placed in the field.
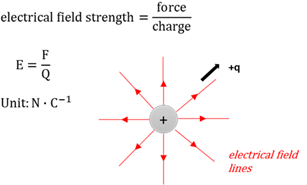
Electric field strenght
The force (F) that a positive unit charge will experience at a point in the field.
Electric motor
An electric motor converts electrical energy into mechanical energy.
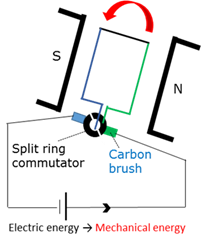
Electrical conductor
Material that can conduct electricity.
Electrical isolator
A material that does not conduct an electric current.
Electrical potential energy
The energy that an electricaly charged object has because of its position in an electric field.
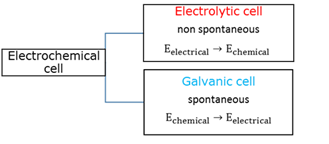
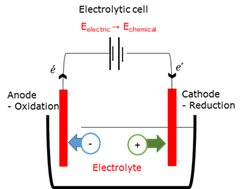
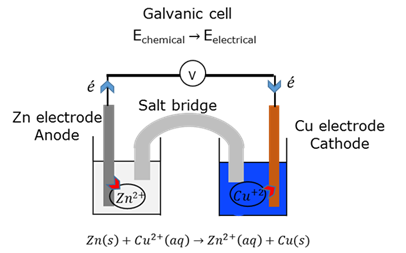
Electrochemical cell
There are two kinds of electrochemical cells - an electrolytic cell converts electrical energy into chemical energy, while a galvanic cell obtains electricity from the cell by converting chemical energy into electrical energy.
Electrochemical reaction
A redox reaction in which chemical energy is converted into electrical energy.

Electrode
An electrical conductor that carries an electric current into and from an electrolyte.
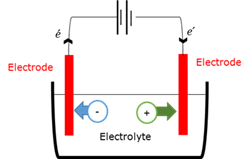
Electrolysis
The chemical process in which electrical energy is converted into chemical energy. Chemical decomposition occurs at the electrodes as the electric current passes through the electrolyte.

Electrolyte
A solution / liquid / dissolved substance that conducts electricity through the movement of ions.
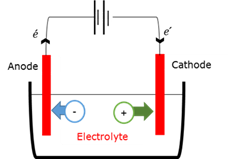
Electrolytic cell
In an electrolytic cell the composition of chemicals is changed when electrical energy from an external source is transferred to the chemicals in a process called electrolysis. The reactions at the electrodes are sustained by a supply of electrical energy being converted into chemical energy.
Electromagnet
A temporary magnet that is formed when an electric current runs through a wire that is wound around a magnetic material like iron. When the current stops the magnet dissapears.

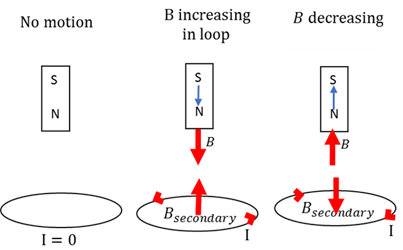
Electromagnetic induction
The induction of an emf and current in a closed circuit when the magnetic flux surrounding the conductor change.
Electromagnetism
The interaction between electric fields and magnetic fields in that a change in the one induces a change in the other.
Electron
Sub atomic particle with a negative charge found in the space around the nucleus.

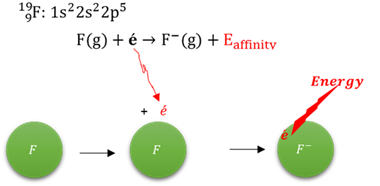
Electron affinity
The energy that is released when an electron is added to a neutral atom in its gas phase to form an ion.
Electron current
The flow direction in which the negatively charged electrons will flow in a circuit, which is from negative to positive.
Electron notation - Electron configuration
A schematic representation of the arrangement of electrons in the orbitals of an atom.
Electronegativity
A measurement indicating how strong an atom in a molecule will attract a shared electron pair towards itself. On the Pauling scale F has the highest value of 4.0, with Cs the lowest at 0.7.
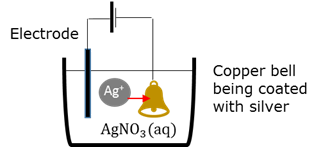
Electroplating
Coating a metal object with another metal by electrolytic deposition . The (positive) coating ions in the electrolyte are attracted by the negatively charged target.
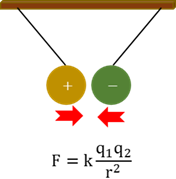
Electrostatic force
The attraction or repulsion forces that charges in an electric field exert on each other.
Electrostatics
The study of charges that are not moving.
Element
A pure substance composed only of one type of atom and which cannot be decomposed into simpler substances by any physical or chemical process.

Elimination reaction
When two atoms or a group of atoms are removed from adjacent carbon groups in a saturated hydrocarbon and two products are formed.

Emf
The total energy supplied per coulomb of charge by the cell.

Empirical formula
The simplest ratio in which atoms of different elements bind to form a molecule.
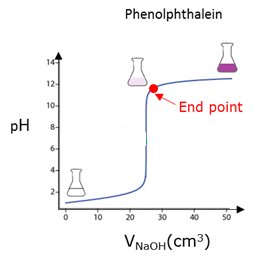
End point
The end point of a titration is reached when the indicator changes colour.
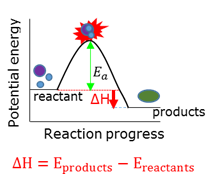
Endothermic reaction
A chemical reaction that requires energy. The products have more potential energy than the reagents had. ∆H is positive.

Enthalpy (∆H)
The net change in chemical potential energy of the system.
Entropy(S)
An indication of the degree of disorder in a system.
Equilibrant
A single force that has the same effect as the resultant of two or more forces, but it is exerted in the opposite direction.

Equilibrium constant for water
Kw (ionic product or ionisation constant of water) is the equilibrium constant for the ionisation of water. Also known as the dissociation constant.
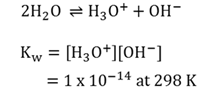
Equilibrium constant Kc
The ratio of the equilibrium concentrations of the products raised to the power of their stoichiometric coefficents and the equilibrium concentrations of the reactants raised to the power of their stoichiometric coefficents.
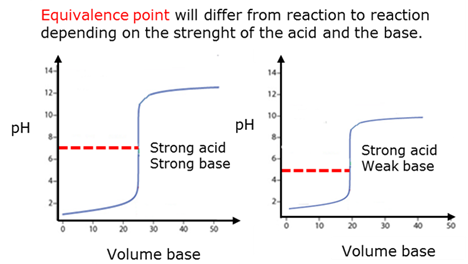
Equivalence point
Also called stoichiometric point of a chemical reaction. The point in a titration where chemically equivalent quantities (equal molar amounts) of an acid and a base have been mixed.
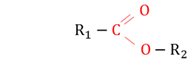
Esters
An organic compound with -C00- as a functional group.
Eutrophication
The process by which ecosystems, like rivers or dams, become enriched with inorganic plant nutrients (nitrogen and phosphorus), resulting in excessive plant growth. Can be accelerated by effluent and leaching of fertilizers from the soil.
Evaporation
Physical change from the liquid phase to the gas phase.
Exothermic reaction
A chemical reaction during which energy is released. The products have less potential energy than the reagents had. ∆H is negative.
External force
The forces that are exerted from outside the system on objects within the system.
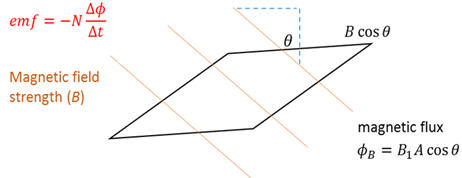
Faraday’s law
An emf is induced in a conductor when the magnetic field around the conductor changes. The magnitude of this induced emf (ε) in an electric circuit is directly proportional to the rate of change of the magnetic flux (Ø) through the circuit.
Ferromagnet
A substance that can be magnetised by a magnetic field and will remain a magnet after the magnetic field has been removed.
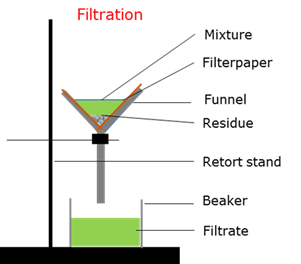
Filtrate
The liquid that is recovered during filtration.
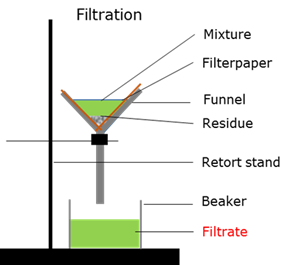
Filtration
A mechanical or physical process to separate a solid precipitation from a liquid by interposing a medium through which only the fluid can pass
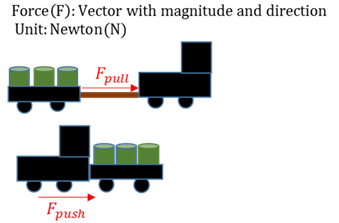
Force
The interaction between two objects in the form of either a pulling or a pushing force.
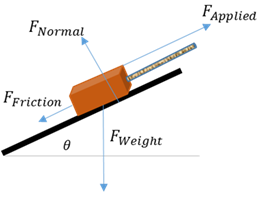
Forces diagram
A sketch of the object of interest with all the forces acting on it drawn as arrows.
Fractional distillation
The extraction of individual components from a mixture by utilising their different boiling points to separate them.

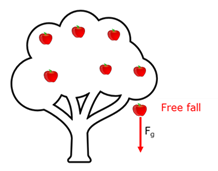
Free fall
The motion of an object when gravitational force is the only force working in on it.
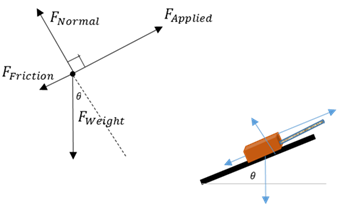
Free-body diagram
The object of interest is drawn as a dot and all the forces acting on it are drawn as arrows pointing away from the dot.
Freezing point
The specific temperature at which a substance changes phases from liquid to solid (the solid phase and the liquid phase are in equlibrium).

Frequency of waves
The number of waves that move past a particular point in one second. Inverse of period (f = 1/T ).
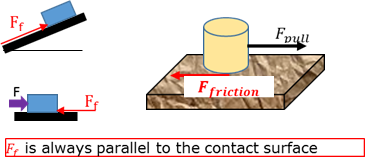
Friction force
The force acting parallel with the contact surface that opposes the motion of an object.
Functional group
An atom, group of atoms, or a bond that determines the physical and chemical properties of a group of organic compounds.
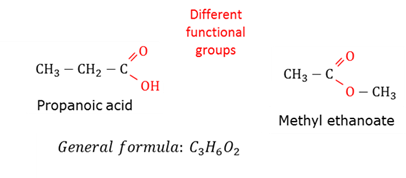
Functional isomers
Molecules with the same molecular formula, but with different functional groups.
Galvanic cell
In a galvanic cell (voltaic cell) electrical energy is obtained from the cell when chemical energy is converted into electrical energy by way of redox reactions.
Gas forming reactions
When one of the formed products in an exhange reaction between an anion and a cation is a gas.
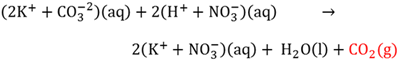
Gas phase
The phase of matter in which the particles have the biggest freedom of movement. Gases fill the whole space of the container in which it is kept.
General formula
A formula that fits all the members of a homologous series.
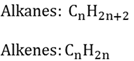
Generator
A device that converts mechanical energy into electrical energy by using Faraday's principle.
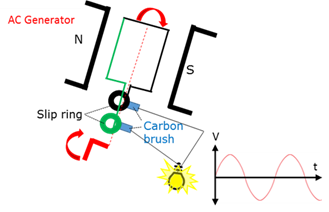
Generator - AC
Generator that produces an alternating current (AC) because it has two split rings.

Gravitational field
A region in space where a mass will experienece a gravitational force. The force field that exist around any body with mass and causes it to have an attraction force on another body with mass.
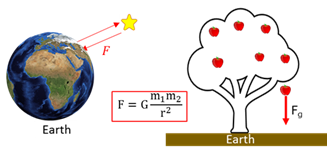
Gravitational force
The attraction force between any two bodies due to their mass.
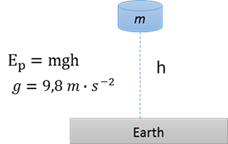
Gravitational potential energy (U or Ep)
The energy an object posesses due to its posistion in the gravitational field relative to a reference point.
Ground state electrons
The state when the electrons occupy the loweste possible energy levels.
Guy Lussac's law
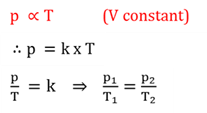
The pressure (p) of an enclosed mass of gas is directly proportional to the absolute temperature (T) at constant volume.
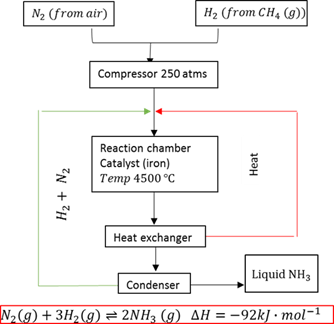
Haber process
The industrial process to manufacture ammonia from nitrogen and hydrogen in the presence of a catalyst.
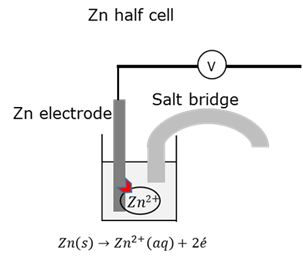
Half cell
A half cell forms one half of a galvanic cell. It consists of an elctrode in a solution of its ions.
Half reaction
During a redox reaction two half reactions take place simultaneously - a reduction half reaction and an oxidation half reaction.
Haloalkane (Alkyl halide)
A carbohydrate in which one or more hydrogens are replaced with a halogen atom (F, Br, Cl or I )
Halogenation
An addition reaction where a halogen attaches to an unsaturated hydrocarbon.

Heat of reaction
(ΔH) The energy absorped or released during a chemical reaction.
Heisenberg's uncertainty principle
The position and the energy of a subatomic particle cannot be determined simultaneously.
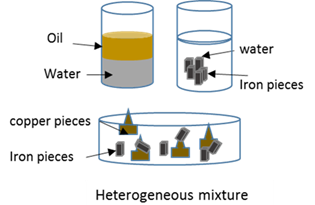
Heterogeneous mixture
A heterogeneous mixture consist of substances that are in different phases, or out of components that can be identified individualy.
Heterogeneous reaction
Reaction where the reagents and products are in different phases.
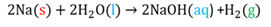
Hetrogenous catalyst
The catalyst and reagents are in different phases.
Homogeneous mixture
All the substances are in the same phase and the different components cannot be identified individualy.

Homogeneous reaction
Reaction where the reagents and products are in the same phase.
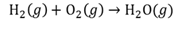
Homogenous catalyst
The catalyst and reagents are in the same phases.
Homologous series
A series of similar compounds that have the same functional group and the same general formula, but where each member differs from the previous member by a single -CH2-unit.
Hund's rule
Electrons fill equal energy orbitals of a sub-shell with their spin in the same direction, before pairing takes place.
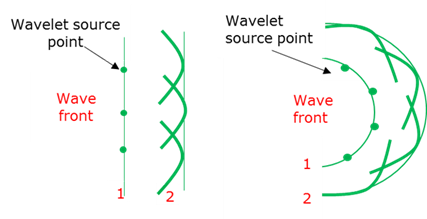
Huygens principle
Each point on a wave front is the source of a new spherical wave. The superpositioning of all the small wavelets will form the new wave.
Hydrated compound
A compound that has a specific number of water molecules per formula unit - For example blue copper sulphate crystals.
Hydration
The process when ions are surrounded by water molecules in a solution.
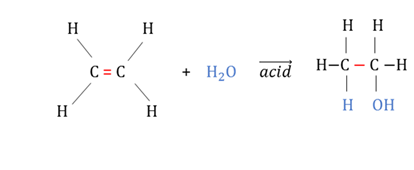
Hydration reaction
An addition reaction between water and an unsaturated hydrocarbon.
Hydride
A compound where hydrogen is bonded to a metal.
Hydro-halogenation
An addition reaction between a hydrohalogen and an unsaturated hydrocarbon. The hydrocarbon becomes more saturated.
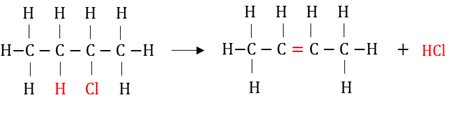
Hydrocarbons
Compounds that consist only of carbon and hydrogen atoms.
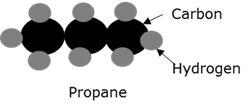
Hydrogenation
An addition reaction between hydrogen and an unsaturated hydrocarbon (alkene or alkyne) in the presence of a catalyst (Ni, Pa, Pt) resulting in the organic compound becoming more saturated.
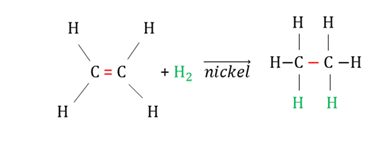
Hydrolysis of a haloalkane
A substitution reaction where a haloalkane reacts with water to form an alcohol.
Hydronium ion
Hydrosphere
All the water on the earth.
Hygroscopic
A substance that attracts water.
Ideal gas
An ideal gas is a hypothetical gas in which the gas molecules have a negligible volume and there are no attraction force between the particles of the gas. It conforms to the general gas equation in all respects.
Ideal gas law
The volume (V), pressure (p) and temperature (T) of a gas is determined by the amount of gas (n).
Impulse
The product of the net force (Fnet) acting on an object and the contact time (∆t) that the force is acting on the object.
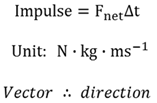
Impulse-momentum theorem
The product of the net force (Fnet) and the time (Δt) that the force acts on the object is equal to the change in momentum (Δp) of the object - (Δp = Fnet x Δt).
Impure substance
A substance consisting of more than one form of matter.
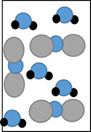
In phase
Points on a wave where the amplitude and direction of the disturbance are the same.

Independent variable
The variable that can cause a change in the dependent variable. On graphs it always appears on the x-axis. The values of the independent variableare selected before the experiement starts.

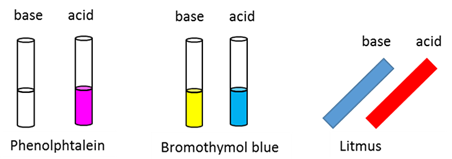
Indicator
A chemical substance that has different colours in basic and acidic solutions.
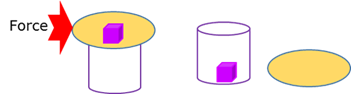
Inelastic collision
A collision in which only momentum is conserved.

Inertia
The property of an object that causes it to resist a change in its state of rest or uniform motion.
Instantaneous speed
The speed at a specific moment and is equal to the magnitude of the instantaneous velocity at that moment.
Instantaneous velocity
A vector quantity of displacement divided by a very small time interval.
Interference
Interference occurs when two or more waves move across each other and effect each other.

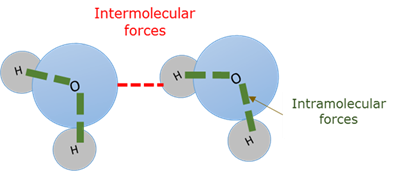
Intermolecular force
Forces of attraction between molecules.
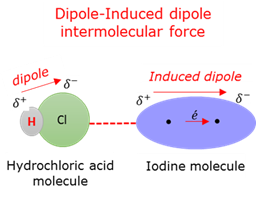
Intermolecular force: Dipole- Induced dipole
Van der Waals intermolecular attraction force between a polar molecule and a non-polar molecule in which a temporary dipole was induced.
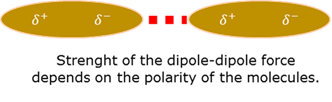
Intermolecular force: Dipole-Dipole
Van der Waals intermolecular attraction force between two polar molecules.
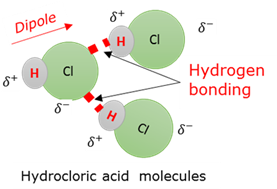
Intermolecular force: Hydrogen bond
A very strong intermolecular dipole-dipole attraction force between molecules consisting of hydrogen and another atom with a high electronegativity value, like oxygen, nitrogen and fluorine.
Intermolecular force: Ion-Dipole force
Intermolecular attraction force between an ion and a polar molecule.
Intermolecular force: Ion-Induced dipole
Intermolecular attraction force that forms when an ion induces a dipole in a non-polar molecule.
Intermolecular force: London force
Weak Van der Waals intermolecular attraction force. Unequal distribution of the electron cloud around big non-polar molecules lead to momentary dipoles forming.
Intermolecular force: Van Der Waals force
Collective name for weak intermolecular forces arising from the interaction of moleculecular dipoles.
Internal force
Forces which the objects within a specific system excert on each other.
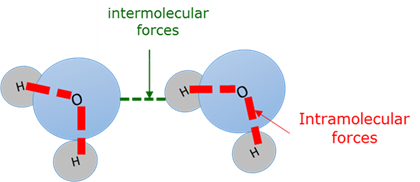
Intramolecular force
Bonding forces between atoms within molecules (Interatomic forces).
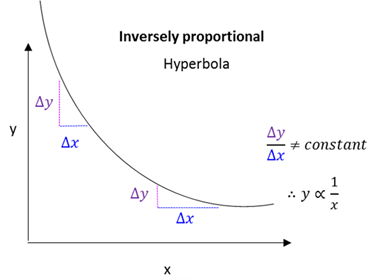
Inversely proportional
When an increase in one variable leads to a decrease in the other variable.
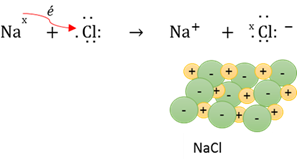
Ion
An ion is a single atom or a group of atoms with a positive or a negative charge; eg. Na+ ; Br- ; NH4+ ; SO2-2
Ionic bond
An electron(s) is transferred from one atom to another to form ions, with subsequent attractive electrostatic forces keeping them together.
Ionisation
A chemical reaction between a substance and water to form hydrated ions.
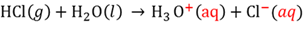
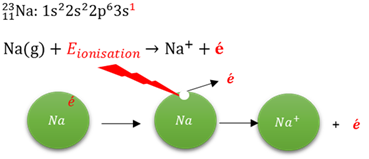
Ionisation energy
The minumum energy needed to remove the first electron from an atom in the gas phase.
Irreversible chemical reaction
A chemical reaction that can only take place in one direction. The reagents react to form the products, BUT the products cannot react with each other.
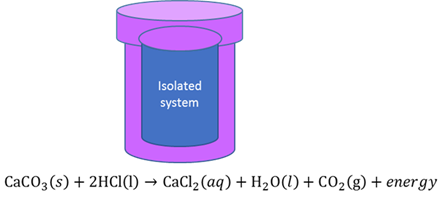
Isolated chemical system
A system where the total mass of the system remains constant during a chemical reaction and NO energy transfer between the system and the surroundings can take place.
Isolated system in physics
A system that does not interact with its surroundings, that is, its total energy and mass stay constant.
Isomer
Molecules that have the same molecular formulae, but different structure formulae.
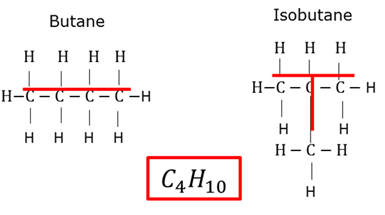
Isotope
Atoms of the same element (same atomic number) but with a different mass number. (Number of protons in the nucleus are the same, but the number of neutrons in the nucleus is different).
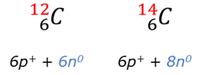
Joule (J)
The unit for Energy (E) or Work done (W). One Joule is the amount of work done on an object if a force of 1 Newton moves the object over 1 meter.
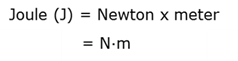
Kelvin
The SI unit for absolute temperature where the scale starts with 0 Kelvin.
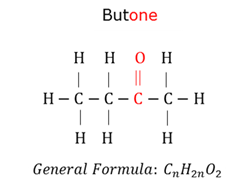
Ketones
Organic compounds with a carbonyl group (-C=O ) as a functional group in the middle of the carbon chain. The name of a ketone ends in -one.
Kilowatt hour (kWh)
Unit used for the consumption of electrical energy, indicating the electrical power (watt) consumed in 1 hour.
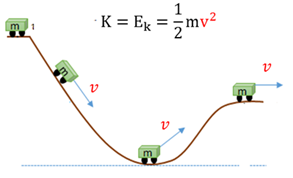
Kinetic energy (K or Ek)
The energy an object posesses as a result of the object's motion(velocity).
Kinetic friction force
The force that opposes the motion of a moving opject relative to the surface.

Kinetic molecular theory
Describes the motion of atoms and molecules.
Latent heat
The energy required to make a substance change phases.
Law of constant proportions
A chemical compound will always consist of the same elements and in the same mass ratios, irrespective of how it is prepared.

Law of reflection
When light is reflected the angle of incidence (i) is always equal to the angle of reflection (r).
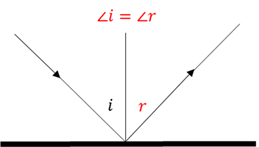
Le Chatelier’s principle
When the equilibrium in a closed system is disturbed (change in pressure, temperature or concentration) the system will re-instate a new equilibrium by favouring the reaction that will oppose the disturbance.

Leach
The process where certain substances are drained out of a bigger assembly by selectively dissolving them.
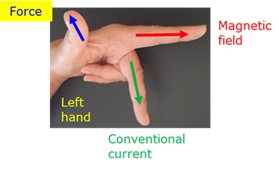
Left hand motor rule (Fleming)
Hold the first finger, middle finger and thumb of the left hand perpendicular to each other. If the first finger indicates the direction of the magnetic field and the middle finger points in the direction of the current in the conductor, then the thumb will point in the direction of the force on the conductor.
Lenz's law
When a changing magnetic field induces a current in a conductor, the direction of the induced current will be such that it produces a second magnetic field which will counter the original changing magnetic field.
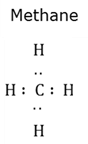
Lewis structure
The valence electrons around an atom or ion are shown as dots or crosses.
Light speed
The speed of light is constant when passing through a given medium, but is different in different mediums.
Line emmision spectra
The spectrum that is obtained when atoms from elements emmit their characteristic wavelengths.

Liquid phase
A condensed state of matter where the particles have restricted movement and have the ability to flow. Liquids take on the shape of the container.
Lithosphere
The outer layer of the earth, consisting of the crust and upper mantle.
Lone pair electrons
Paired valence electrons which do not form part of the chemical bond.
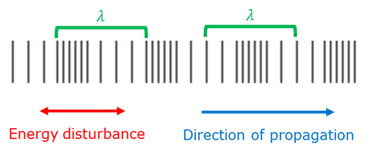
Longitudinal wave
Consecutive pulses where the disturbance is in the same direction as the wave.
Lost volts
An indication of the amount of work done per unit charge to overcome the internal resistance of the battery.
Macromolecule
A molecule that consist of a large number of atoms.
Magnet
An object with a pair of opposite magnetic poles, called North and South.
Magnetic field
The region in space where a magnet or ferromagnetic material will experience a magnetic force (non-contact).

Magnetic field lines
Schematic representation that is used to show the shape and direction of a magnetic field. The convention is that the direction of the magnetic field lines is the direction into which the N pole of a compass will show when it is placed in the field.
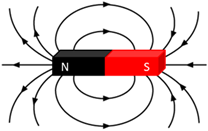
Magnetic flux
The number of magnetic field lines passing through a closed area. It is calculated as the product of the number of turns on the coil and the flux through the coil.
Magnetic flux density
The magnetic flux density (magnetic field strength) is the magnetic force which a conductor will experience in a magnetic field if a current is flowing through the wire. The magnetic flux (F) passing through a loop of area A in the presence of a uniform magnetic field B, is F = BAcosθ, where θ is the angle between the magnetic field B and the normal to the loop A.
Magnetosphere
The space where the Earth's magnetic field will be experienced.
Manometer
An apparatus that is used to measure the pressure of gases by measuring the different heights of a liquid in a U-tube.
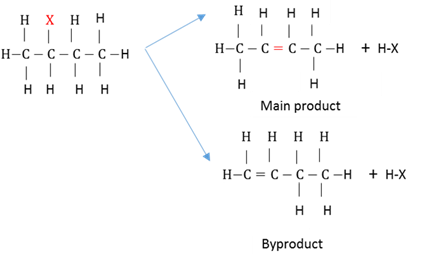
Markovnikov's rule
When an unsymetrical reagent is added to an unsymmetrical alkene, the hydrogen will bond to the carbon with the greater number of attatched hydrogens and the X atom will bond to the more substituted carbon.
Mass
Die amount of matter (quantity of atoms or molecules) that a substance is made of.
Mass number
Mass number (A) is the sum of the protons and neutrons in the nucleus of an atom.

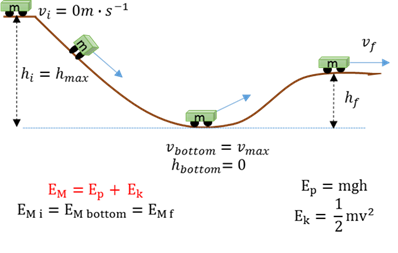
Mechanical energy (Em)
The total mechenical energy is the sum of the potential and kinetic energy at a point.
Melting point
The temperature at which a substance changes phases from solid to liquid (the solid phase and the liquid phase are in equilibrium).
Metallic bond
Positive metallic atom rests are kept together by a sea of delocalised electrons swarming around them.
Metalloids
Substances with both metal and non-metal properties.
Mixture
A mixture consist of various pure substances that does not react chemicallywith each other and which can be separeted with physical methods.
Molar concentration (molarity)
The mole (n) solute per volume of the solution.
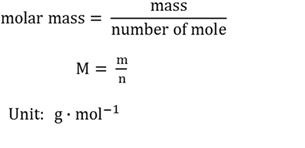
Molar mass
Mass (m) in gram of one mole (n) of a substance.
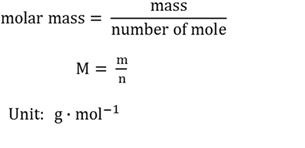
Molar volume
1 mole of any gas occupies 22,4 cubic decimeters at STP.
Molarity
The molar concentration of a substance and indicates the number of moles solute per volume of solution in dm3 .
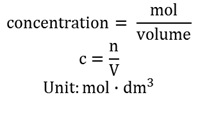
Mole
The amount of substance that contains as many entities (6.022 x 1023) as there are atoms in 12g of carbon-12.
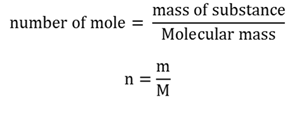
Molecular formula
Gives the ratio and quantity of the atoms of each element in the molecule.
Molecule
A neutral compound consisting of two or more atoms that are bound to each other with chemical bonds and which exist as a unit.
Momentum
The product of the mass (m) and velocity (v) of an object.

Monochromatic light
Light of a single colour (wavelength).
Monomer
Small organic molecules that can be bonded covalently to each other in a repeating pattern to form a polymer.

Monoprotic acid
An acid that can donate only one proton (H+) per acid molecule.

Motor effect
The phenomenon that a current-bearing conductor experiences a force when it is placed in a magnetic field.

Negative catalyst
A catalyst that increases the activation energy of a reaction and therefore decreases the reaction rate.

Neutralisation
A chemical reaction between an acid and a base to form a salt and water.
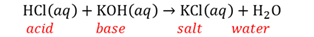
Neutron
Sub atomic particle with no charge, found inside the nucleus.
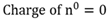
Newton’s first law
An object continues in its state of rest or move a with constant velocity in a straight line, unless it is acted upon by an unbalanced (net or resultant) force.
Newton’s law of Universal Gravitation
Every object in the universe attracts every other object with a force (F) that is directly proportional to the product of their masses (m) and inversely proportional to the square of the distance (r) between their centres.
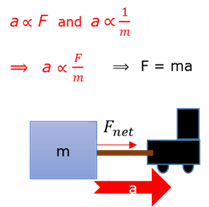
Newton’s second law
When a nett force (Fnet) is applied to an object of mass (m), the object will accelerate (a) in the direction of the nett force. The acceleration is directly proportional to the nett force and inversely proportional to the mass.
Newton’s second law to momentum
The net force (Fnet) acting in on an object is equal to the rate (∆t) of change in momentum (∆p) of the object in the direction of the resultant/net force.
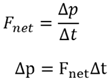
Newton’s third law
When object A exerts a force on object B, object B simultaneously exerts a similar force on A which is of the same magnitude, but in the opposite direction. (Known as action-reaction pairs).

Noble gas electron structure
In a noble gas electron structure there are no unpaired or empty orbitals in the valence level of the atom.
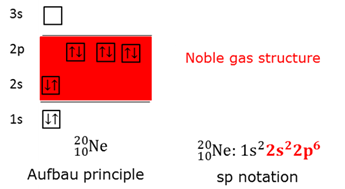
Nodal lines
Areas where no interference is visible due to destructive interference.
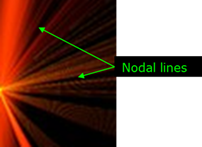
Non-conservative forces
If the work done by a force to move an object between two points is dependent on the path of motion, the force is called non-conservative. The net work done by a non- conservative force to move an object around a closed path (starting and ending at same point) is NOT zero.

Non-contact force
Forces that objects can exert on each other over a distance.
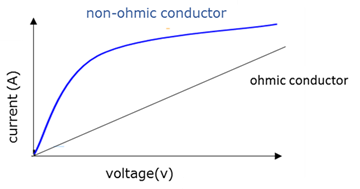
Non-ohmic conductors
A condutor that does not obey Ohm's law. The ratio V/I is not constant (the current does not increase evenly with an increase in voltage).
Non-polar molecule
Two atoms that are covalently bonded to each other. The bonding electron pair is shared equally between the two atoms.
Non-renewable energy
Energy sources that are consumed quicker than they can be formed - Petroleum; Natural gas; Coal; Uranium; etc
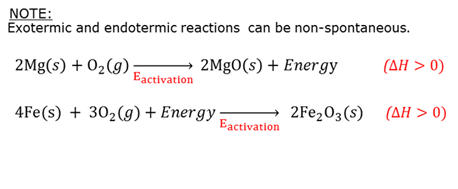
Non-spontaneous reaction
A reaction that will not take place on its own. Some energy is needed to start the reaction and then it can continue on its own.
Non-uniform electric field
The magnitude of the electric field strength is not constant throughout the field and a charge will not experience the same force at every point in the field.

Non-uniform magnetic field
A magnetic field where the field strength and direction is different at different points in the field.
Normal force
A perpendicular reaction force excerted by the surface on an object when that object is in contact with the surface.

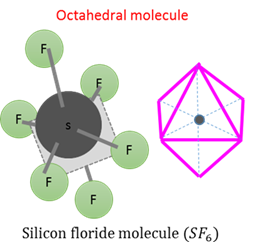
Octahedral molecular form - AX₆
Octahedral molecular form is obtained when four atoms form a central flat quadrant and the other atoms form two pyramids, one above and one below the central quadrant. The bonding angles are all 90°.
Octet rule
An atom (except hydrogen) will strive to form bonds with other atoms or ions until the nucleus is surrounded by 8 valence electrons.
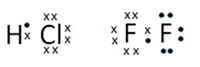
Ohm (Ω)
Unit of electrical resistance. One ohm is the electrical resistance between two points in an electrical circuit if the potential difference between the points is one volt and the current flowing is one ampere.

Ohmic conductor
A conductor that obeys Ohm's law. The ratio V/I is constant (the current increases evenly with an increase in voltage) at a constant temperature.
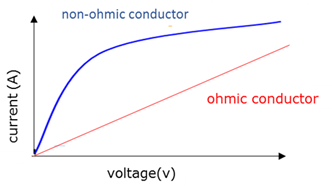
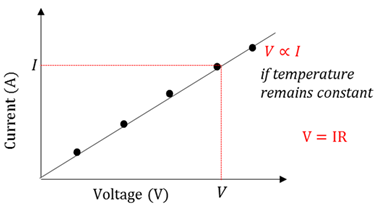
Ohm’s Law
The current through a conductor is directly proportional to the potential difference across the conductor at constant temperature.
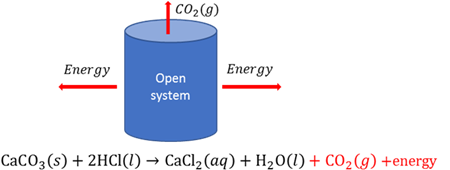
Open chemical system
A system where energy and matter can be given to or be taken from the surroundings.
Open circuit
A circuit is open if an electric current cannot flow through the circuit.

Optical density
The property of a medium that indicates to what extent the medium will restrain the speed of light.
Optical medium
Any medium through which light can propogate (move).
Orbital
The region in an atom where the probability to find an electron is the highest.
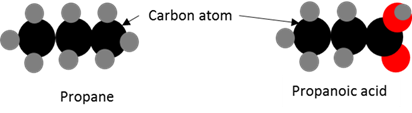
Organic molecules
Molecules that contain carbon atoms.
Ostwald process
The chemical process for making nitric acid (HNO3)

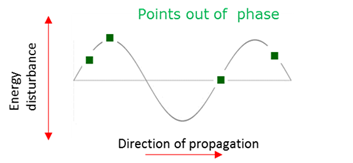
Out of phase
Points on a wave where the amplitude and/or direction of the disturbance are not the same.
Oxidation
The loss of electron(s) by a molecule, atom or ion during a reaction.
Oxidation agent
The reagent that oxidizes the other reagents. In this process the oxidation agent itself undergoes reduction - gains electrons.

Oxidation number
A number indicating the number of electrons that an atom in a compound has lost or gained during a reaction.
Oxidation reaction
The half reaction in which the reagent loses electrons (is oxidised). The oxidation number of that reagent will increase.

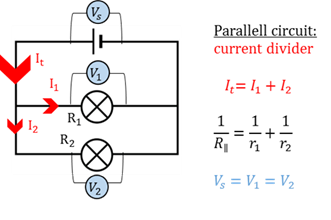
Parallel circuit
A parallel circuit allows the current to go through different branches at the same time.
Pascal
The unit for pressure. A pressure of 1 Pa is exerted on a surface if a force of 1N acts on an area of 1 square meter.
Pauli's exclusion principle
There can be maximum two electrons per orbital on the condition that their spin is opposite. No two electrons of an atom can have the same quantum numbers.
Pauling's scale
A numerical scale representing an atom's tendency to pull the bonding electron pair closer to itself (electronegativity scale).
Period of waves
The time it takes to complete one full cycle of a wave. The inverse of frequency ( T = 1/f).
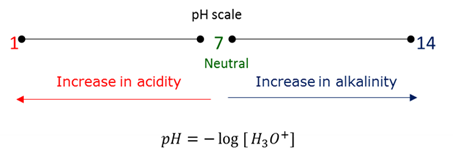
pH
The pH scale is an indication of the relative acidity of the solution. It is calculated by using the concentration of the hydronium ions in the solution.
Phase equilibrium
When the forward and reverse phase changes take place at the same rate (are in balance).
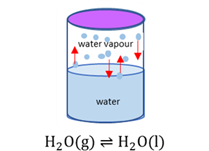
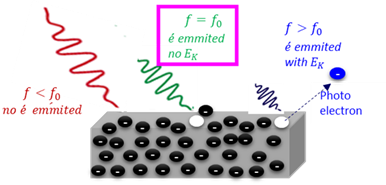
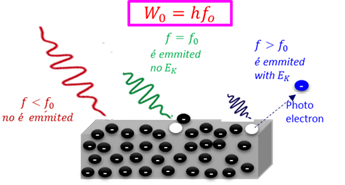
Photo electron
An electron which is released from the surface of a metal when the metal is irradiated by electromagnetic radiation of a frequency larger than the treshold frequency.
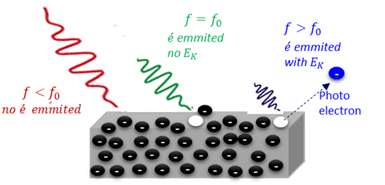
Photoelectrical effect
The ejection of electrons from certain metals when they are exposed to light with a specific frequency.
Photon
The energy parcel (quantum) of electromagnetic radiation that moves with the speed of light, but has no mass.
Physical change
A physical change is a temporary change which does not alter the chemical nature of the substance - no new chemical substances are formed.

Physical reaction
No new substances are formed. The substance only changes phase.
Polar molecule
A molecule where the bonding electrons are not shared equally between the atoms. The shift of the electron pair towards one of the atoms leads to the formation of a dipole.

Polymer
A large molecule composed of smaller monomer units bonded covalently in a repeated pattern.
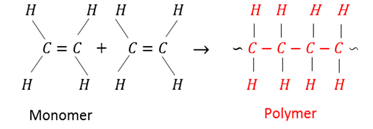
Polymerisation
A chemical process where monomers bond covalently to each other to form a polymer.
Polyprotic acid
An acid that can donate two or more protons per acid molecule.
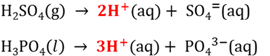
Position
Position is always taken relative to a reference point. Can be positive or negative.
Positional isomers
Molecules with the same molecular formula, but the functional group or side chain is in a different position.
Positive catalyst
A catalyst that decreases the activation energy of a reaction and therefore increases the reaction rate.
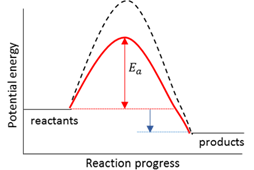
Potential difference
The difference in electrical potential energy between two points. It is determined by the work done to move a charge from the one point to the other point.
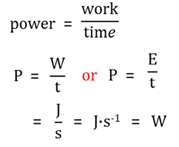
Power
The rate at which work is done, or the rate at which energy is transfered..
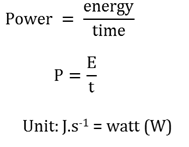
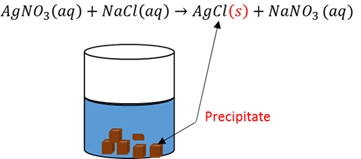
Precipitation
When two solutions are added together and one of the formed products is insoluble it forms a solid precipitate.
Pressure
The force exerted per unit area (1 Pa = 1 N/m²)
Products
The new substances that form when the reagents react with each other during a chemical reaction.

Projectile
An object onto which the only force that acts in on it is gravitational force.
Protolysis
A chemical reaction in which proton (H+) transfer takes place.
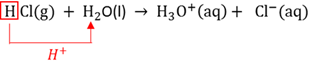
Proton
Sub atomic positively charged particle found inside the nucleus of an atom.

Pulse
A single energy disturbance.

Pure substance
A pure substance consist of only one form of matter with spesific physical and chemical properties and fixed composition.
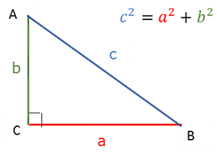
Pythagoras
In any right angled triangle the square of the hypotenuse is equal to the sum of the squares of the other two sides.
Quantisation of charge
Any charge in the universe are multiples of the elementary charge (charge of an electron).
Radioactivity
Emmision of energy and/or particles from an unstable atomic nucleus to create a more stable atomic nucleus.
Rate of reaction
The change in the concentration of reagents or products per unit time.
Ray diagram
A sketch showing the path of a light ray through different media.
Reactants
The chemicals that react with each other when the reaction starts.

Reaction surface
The area of a reagent that can come into contact with the other reagents for a reaction to occur between them.
Real gas
In a real gas the molecules have volume which contribute to the volume of the gas and there are force interactions between the molecules. At extreme conditions a real gas deviates from the universal gas equation.
Red shift
Doppler effect. A shift in the longer wavelengths (red end of spectrum) when a light source moves away from the observer.
Redox reaction
A reaction in which electron (e-) transfer takes place from one chemical substance to another chemical substance and therefore the oxidation numbers of the participating atoms will change.

Reducing agent
The reagent that reduces the other reagents. In this process the reduction agent itself undergoes oxidation - loses electrons.

Reduction
The gaining of electrons by a molecule,atom or ion during a reaction.
Reduction reaction
The half reaction in which the reagent gains electrons (is reduced). The oxidation number of that reagent will decrease.

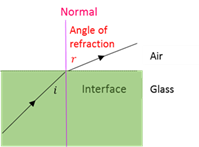
Refraction index
Refraction index of a transparent medium is the ration of the speed of light in a vacuum (v₁) to the speed of light in that medium (v₂).
Refraction of light
The changing of the direction of light as it passes from one optical medium to another medium with a different optical density.

Relative atomic mass
The mass of an atom relative to the mass of a carbon-12 atom.
Relative formula mass
The sum of the atomic masses of all the atoms in a molecule of the substance and is measured in atomic mass unit (u).
Renewable energy
Energy derived from natural resources that are not used up - Hydropower; Geothermal; Wind; Solar; Biomass; etc

Residu
The solid precipitate that remains after filtration.

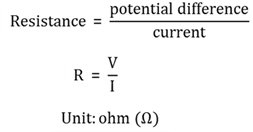
Resistance
The characteristic of matter to resist the flow of an electric current if a potential difference is applied across it.
Resistor
An electrical component that is designed to resist the flow of an electric current.
Resultant
A single vector quantity that has the same effect as the other vectors combined
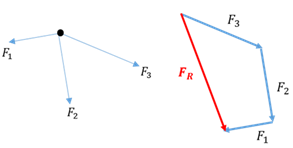
Reversible chemical reaction
A chemical reaction in which the reagents react to form products and then the products react to form the original reagents.

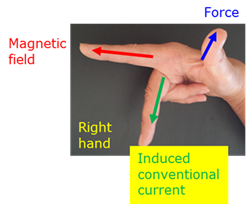
Right hand dynamo rule
Hold the first finger, middle finger and thumb of the right hand perpendicular to each other. If the first finger indicates the direction of the magnetic field and the thumb the direction of movement, then the middle finger will give the direction of the induced conventional current.
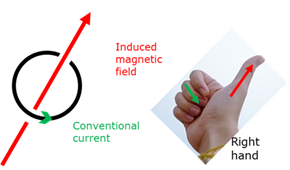
Right hand rule - single winding
If you bend the fingers of your right hand in the direction of the conventional current, then your stretched thumb will indicate the direction of the induced magnetic field.
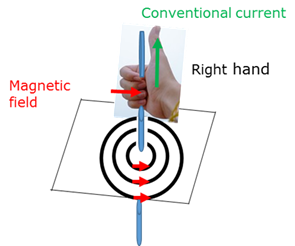
Right hand rule - solenoid
If you hold the solenoid in your right hand with your bent fingers in the direction of the conventional current, then your stretched thumb will point in the direction of the N-pole of the solenoid.

Right Hand rule - straight conductor
Hold the conductor in your right hand with the thumb pointing in the direction of the conventional current. The direction in which the fingers curl, indicates the direction of the magnetic field (field lines).
Root mean square current
The RMS current, Irms for an alternating current (AC) is equal to the direct current (DC) current that uses the same amount of energy as the alternating current.
Root mean square potential difference
The RMS potential difference, Vrms for an alternating current (AC) is equal to the direct current (DC) potential difference that uses the same amount of energy as the alternating current.
Root mean square values
A method to calculate the effective values of an alternating voltage or alternating current, taking into account that they continually change from a positive maximum through zero to a negative maximum. (The average will be zero).
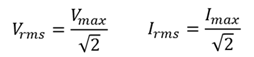
Salt
A sustance in which the hydrogen of an acid is replaced by a cation

Saturated carbohydrate
A hydrocarbon chain in which all the bonds between C-atoms are single bonds.

Saturated solution
A solution in which an excess solute has been dissolved in the solvent.
Scalar
A physical quantity that has magnitude only - time, mass, length, volume, energy, charge, temperature, etc.
Semiconductor
A substance that can only conduct electicity under certain specific conditions. Used for the control of electric currents in electronics.
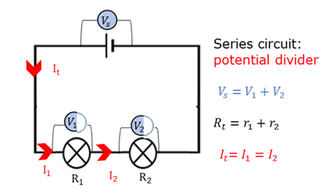
Series circuit
In a series circuit the current has to flow through all the components one after the other.
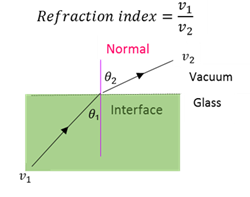
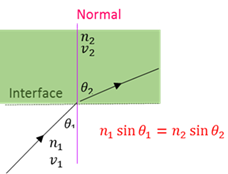
Snell’s law
When light passes from a medium with refraction index n₁ to another medium with refraction index n₂ the relationship between the angle of incidence (θ₁) and the angle of refraction (θ₁) is : n₁sin θ₁ = n₂sinθ₂
Solenoid
A solenoid consist of a large number of coils of conducting wire that are wound into a unit. When a current flows through it, it creates a magnetic field.

Solid phase
The most dense phase of matter where particles are bonded to each other. Solids retain their shape irrespective of the container.
Solubility
The amount of solute that can dissolve in the solvent at a specific temperature.
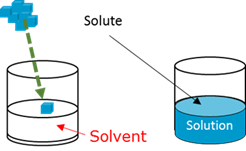
Solute
The substance that is dissolved in the solvent to form a solution.
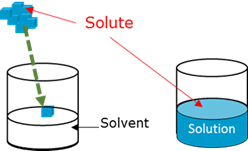
Solution
The final mix of solute in the solvent.
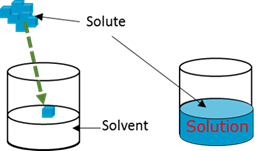
Solvent
The liquid substance into which another substance is dissolved to form a solution.
Specific heat capacity
The amount of energy required to increase the temperature of 1 gram of a substance by 1 °C.
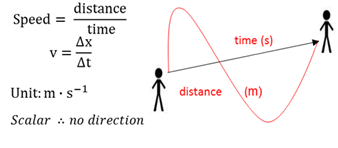
Speed
A scalar quantity for the rate of change in distance.
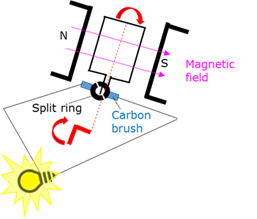
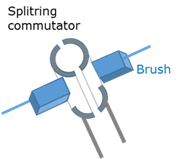
Split ring commutator
A component in the electric motor that reverses the current in the coil every half cycle to ensure that the torque continue acting in the same direction.
Spontaneous reaction
A reaction that will take place on its own (spontaneously).
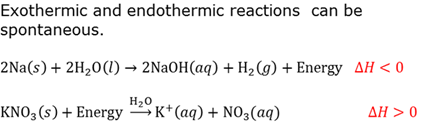
Standard electrode potential
The potential difference between a specific half cell and the standard hydrogen half cell.
Standard hydrogen electrode
The electrode used as standard to determine the redox potentials of other elements.

Standard solution
A solution of which the concentration is known.
Standardise
To standardise a solution means you use a solution with known consentration to determine the consentration of the unknown solution.
Static equilibrium
An equilibrium where no further changes occur, not on micro or macro level.
Static friction force
The force relative to the surface that opposes the attempts to bring a stationary object into motion.
STP
Standard reference conditions - Standard temperature = 0 °C (273 K); Standard pressure = 1 atmosphere (101,3 kPa)
Strong acid
An acid that ionises completely in water to form a high concentration of hydronium ions.
Strong base
A base that dissosiates/ionises completely in water to form a high concentration of OH- ions.
Structural formula
Shows how the atoms in a molecule are linked to each other. All bonds are shown as lines between the atoms.

Subatomic particles
Very small particles that make up an atom.

Sublimation
A phase change where a substance changes directly from a solid into a gas without going through a liquid phase.

Substitution reaction
A reaction in which an atom or group of atoms in a saturated hydrocarbon is substituted by another atom or group of atoms to form a different saturated hydrocarbon and a byproduct.

Superposition
The addition of the amplitudes of two pulses that occupy the same space at the same time.
Suspension
A heterogenuous mixture where solid particles float in a liquid.
Synthesis
The production of more complex chemical compounds when simpler substances react.
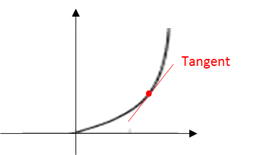
Tangent
A line that touches a curve tangentialy at one point
Temperature
The temperature of a substance is an indication of the average kinetic energy of the particles in the substance.
Tension
The force that is exerted through an object that can stretch (rope, wire, spring).
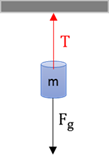
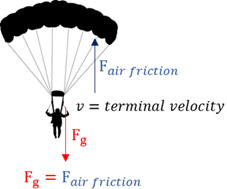
Terminal velocity
The constant final velocity that a falling object attains when the downward gravitational force is equal to the upward air resistance.
Tetrahedral molecular form - AX₄
Tetrahedral molecular form is obtained when four atoms are bonded to a central atom with bonding angles of 109,5° each.

Thermal isolator
A material that does not allow heat energy to be transferred easily through it.

Threshold frequency
The minimum frequency (energy) of light required to release an electron from the surface of a material (E = hf).
Titration
An experimental procedure where a liquid with known concentration is used to detrmine the unknown concentration of another liquid.

Total internal reflection
Total internal reflection occurs when light moves from an opticaly more dense to an opticaly less dense medium and the angle of incidence is greater that the critical angle.

Transverse wave
Consecutive pulses where the particles of the medium (energy disturbances) move perpendicular to the propagation direction of of the wave.

Triangle rule of forces
If three forces in the same plane acting in on the same point are in equilibrium, then their magnitudes and directions can be represented as the sides of a closed triangle when they are placed in sequence.

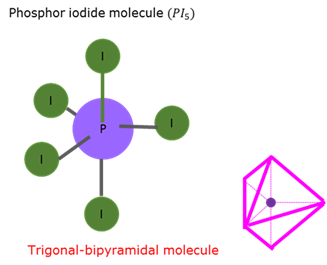
Trigonal bipyramidal molecular form - AX₅
Trigonal bipyramidal molecular form is obtained when three atoms form an even side triangle (angles 120°) in a flat plane, with a fourth atom above the plane to form a pyramid. The bond angle between the fourth atom and the plane is 90°.
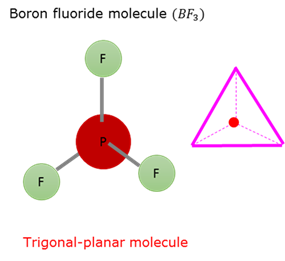
Trigonal planar molecular form - AX₃
Trigonal planar molecular form is obtained if three atoms in a flat plane bond to a central atom. The bond angle between these atoms and the central atom is 120°.
Triple bond
Covalent bond where two atoms share 6 electrons (three electron pairs).

Triprotic acid
An acid that can donate three protons per acid molecule.

Ultra-sound
Sound with frequencies between 20 kHz and 100 kHz.
Uniform electric field
The magnitude of the electric field strength is constant throughout the field and a charge will experience the same force at every point in the field.
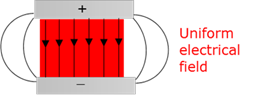
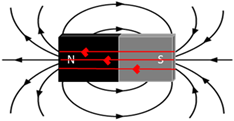
Uniform magnetic field
A magnetic field where the field strength and direction is constant at all the points in the field.
Uniform motion
Motion in a straight line where the speed of the object remains constant (no acceleration).
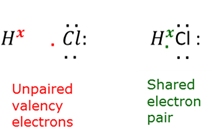
Unpaired valence electron
A valence electron that is available to be shared to form a chemical bond.
Unsaturated carbohydrate
Compounds with one or more multiple bonds between C atoms in the hydrocarbon chain.

Vacuum
A closed space with no matter in it.
Valence
The number of electrons that can take part in a reaction.
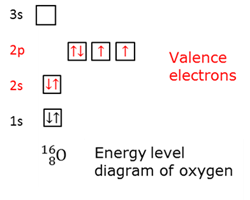
Valence electrons
The electrons in the outer main energy level of an atom.
Vapour pressure
The pressure exerted by a vapour at equalibrium with its liquid in a closed system.
Vector
A physical quantity with both magnitude and direction - displacement, weight, force, magnetic field strength, etc.
Velocity
A vector quantity for the rate of change of displacement.
Viscosity
A measure of a liquids ability to flow.
Volt (V)
A potential difference of 1 V means that 1 joule of work is done per coulomb of charge. ( 1 V = 1 J/ C)
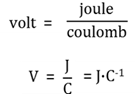
Voltmeter
A voltmeter measures the potential difference between two points in a circuit. It is always connected in parallel.

Watt (w)
The unit for power. One watt (W) is the amount of power used to do work(energy transfer) of 1 joule in 1 second.
Wave
A wave is consecutive pulses where the particles of the medium move in the direction of the energy disturbance, but does not move along with the wave.

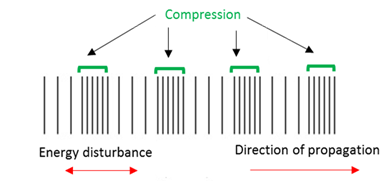
Wave compression
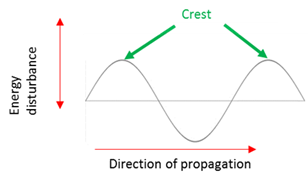
Wave crest
The maximum positive disturbance of a particle from the rest/equilibrium position.
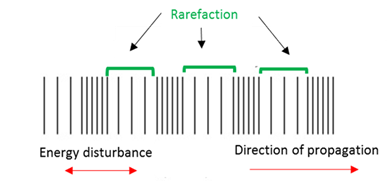
Wave rarefaction
Wave speed
The product of frequency (f) and wavelength (ג) of a wave (v = f x λ ).
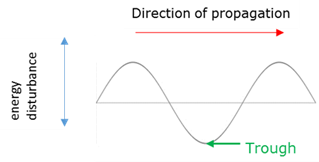
Wave trough
The maximum negative disturbance of a particle from the rest/equilibrium position.
Wave/particle duality of light
Light exhibits properties of both particles and waves. The particle nature explains the photo-electric effect, while the wave nature explains diffraction and interference.
Wavelength - Longitudinal wave
The wavelength (ג) of a soundwave is the distance between two consecutive compressions or rarefactions (expansions).
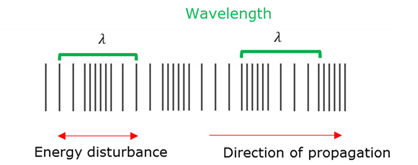
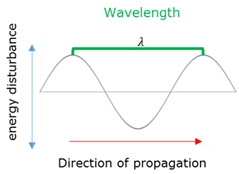
Wavelength - Transverse wave
The wavelength (ג) of a lightwave is the distance between two consecutive points that are in phase (eg. crest to next crest)
Weak acid
An acid that ionises incompletely in water to form a low concentration of hydronium ions)
Weak base
A base that dissociates incompletely in water to form a low concentration of OH- ions.
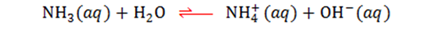
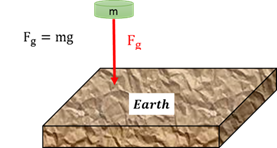
Weight (Fg)
The gravitational force that the earth excerts on any object on or near its surface.

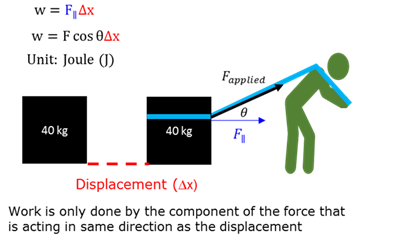
Work
The work (w) done on a object by a constant force F, is F∆xcosθ, where F is the magnitude of the force, ∆x the magnitude of the displacement and θ the angle between the force and the displacement.
Work function
The minimum amount of energy (Wₒ) needed to emit an electron from the surface of a metal.
Work-energy theorem
The net work done by a resultant/net force on an object is equal to the change in the kinetic energy of the object .
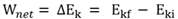
Yield
A measure of the extent of the reaction, by comparing the amount of the reagents consumed against the amount of product that formed.
Zaitzev's rule
At dehidrogenation or dehalogenation, if more than one product is formed, the main product will be the alkene with the highest subsitituted chain. (The H will be removed from the C-atom with the fewest H-atoms.)